The digitalisation of asset maintenance in high-risk industries has reduced unplanned downtime and increased operational efficiency but, as Vysus’ Senior Maintenance & Reliability Consultant Robert Delgado explores, advances in artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning is enabling operators to go further - evolving their maintenance model from a reactive to prescriptive maintenance approach.
With increasing regulatory scrutiny of asset maintenance and inspections, operators know that they must do more to clear maintenance backlogs and have more robust processes in place for understanding, managing, and communicating maintenance risks. While most have moved from a reactive approach to maintenance to developing preventative and condition-based maintenance cultures there is more they can do to eliminate the risk in this area.
With AI operators can automatically analyse historical and real-time data across thousands of sensors, in the context of current operating conditions, to identify maintenance trends, flag areas requiring attention, and implement an effective and targeted maintenance programme.
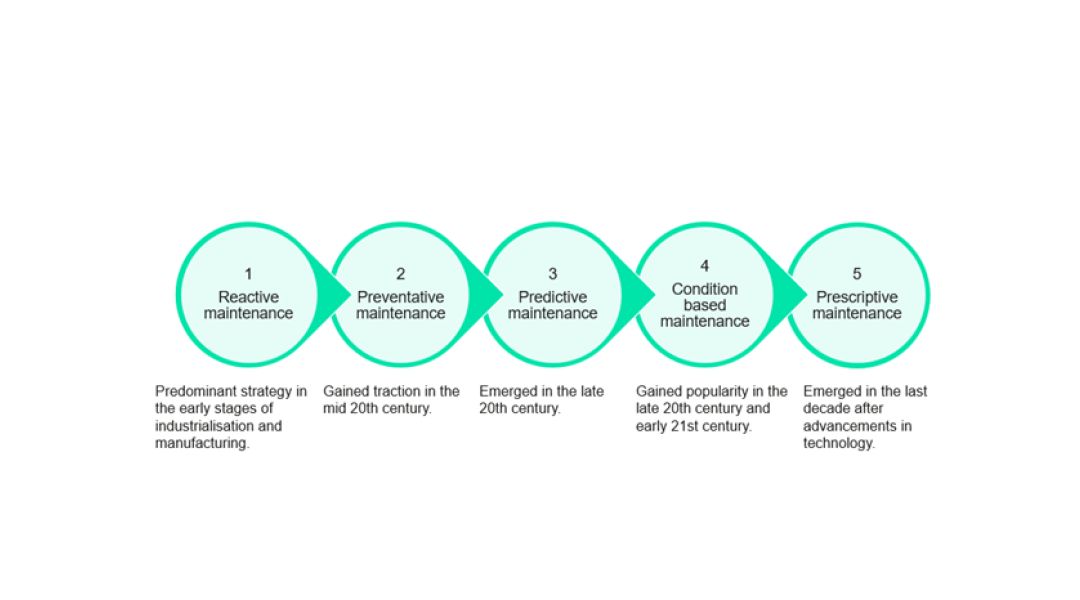
There are five key steps in the evolution of maintenance management from reactive to prescriptive maintenance.
These maintenance strategies are not mutually exclusive, and many organization’s employ a combination of strategies tailored to their specific assets, operational requirements, and industry best practices.

Numerous clients have progressed forward and adopted a combination of the proposed strategies into their operations.
Reactive maintenance: Maintenance actions are taken only after an asset has already failed or experienced a malfunction.
Preventive maintenance: Regular, scheduled inspections, servicing, and maintenance activities are undertaken to prevent equipment failures and breakdowns before they occur.
Predictive maintenance: Data, technology, and analytics are used to predict equipment failures and proactively schedule maintenance activities only when needed.
Condition based maintenance: The condition of equipment and machinery is monitored in real-time to determine when maintenance is needed.
Prescriptive maintenance: AI and algorithms are used to analyse a wide range of data to prescribe the optimal maintenance actions to take on an asset at a given time. This maximises asset performance based on its current condition, history and operating context. Prescriptive maintenance continuously learns from the outcomes of the prescribed actions, updating its models and improving the accuracy of future predictions and recommendations.
Why should high-risk industries embrace prescriptive maintenance technologies?
Prescriptive maintenance provides greater assurance, compliance and risk reduction than the benefits of either a preventative or condition-based approach.
A data-driven maintenance culture, powered by AI and machine learning helps to deliver enhanced operational efficiency faster with minimal unplanned downtime and optimised maintenance schedules. The ability to quickly identify potential safety and environmental hazards and take preventative action also improves compliance.
Continuously monitoring asset health and having an effective maintenance schedule in place extends asset lifespan by mitigating degradation while maintenance costs are in turn reduced through eliminating unnecessary preventative maintenance and minimising costly reactive maintenance.
Prescriptive maintenance allows budgets to be allocated in the right areas reducing the unit cost of maintenance, less OT (Over Time), lower material costs, and reduced labour costs.
By predicting potential failures earlier and prescribing actions to prevent them, prescriptive maintenance helps ensure that assets remain operational and reliable for longer periods, minimizing unplanned downtime.
An example of prescriptive maintenance in action
A manufacturing plant has several critical machines on the production line. The machines are equipped with sensors that monitor parameters such as temperature, vibration and pressure.
Sensor data, along with historical maintenance records and operational parameters are continuously collected and fed into the prescriptive maintenance system. The prescriptive maintenance system uses machine learning algorithms and data analytics techniques to analyze the collected data, identifying patterns and trends that could indicate potential failures or performance degradations. Based on the analysis, the system can predict for example, that a specific bearing in one of the machines is likely to fail within the next two weeks due to increased vibration levels and temperature readings. The system prescribes a maintenance action to replace the bearing or adjust the lubrication system to extend the bearing's lifespan. The system records the outcome of the prescribed action and updates its models and algorithms accordingly. The system learns and improves its predictive capabilities.
At Vysus, we’ve supported operators to reduce operating costs by 40% and improve asset availability and uptime by 20%. Learn more about how we can improve your performance here.
